Implementing VMware SRM for Disaster Recovery: A Step-by-Step Overview
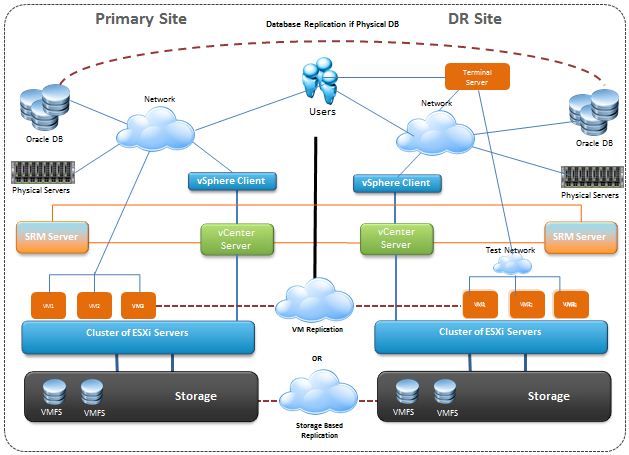
As part of our ongoing IT infrastructure resilience efforts, I recently completed the implementation and configuration of VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) between our production site and a designated Disaster Recovery (DR) site. This project was a key milestone aimed at enhancing our organization's business continuity plan, ensuring critical workloads can failover to a secondary site seamlessly in the event of a disaster.
Project Scope
- Installing and configuring VMware SRM at both production and DR sites.
- Setting up storage replication using NetApp ISCSI storage.
- Testing failover and failback procedures to validate the solution.
1. Environment Preparation
Before diving into SRM-specific configurations, I ensured that both sites had the necessary infrastructure in place:
- vCenter Server Instances: Deployed and configured one vCenter Server at the production site and another at the DR site.
- ESXi Hosts: Clusters at both sites were verified for compatibility and resource availability.
- Networking: Consistent virtual networking was ensured between the two sites to avoid IP conflicts and simplify recovery mapping.
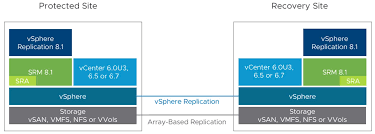
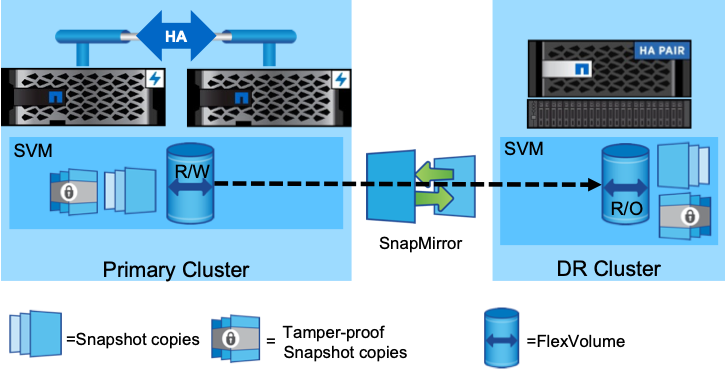
2. NetApp ISCSI Storage Configuration
Storage replication was set up using NetApp's native snapshot and SnapMirror technology:
- Configured ISCSI target LUNs on NetApp at both sites.
- Implemented SnapMirror replication to ensure block-level data replication between the production and DR storage arrays.
- Verified replication schedules, consistency groups, and volume mappings.
This layer was critical, as SRM leverages the underlying storage replication to synchronize VM data between sites.
3. SRM Installation and Pairing
- Installing VMware Site Recovery Manager on both vCenter servers.
- Pairing the SRM instances using the Site Pairing wizard in the vSphere Client.
- Configuring array-based replication adapters (SRA) specific to NetApp, allowing SRM to interact directly with the SnapMirror replication mechanism.
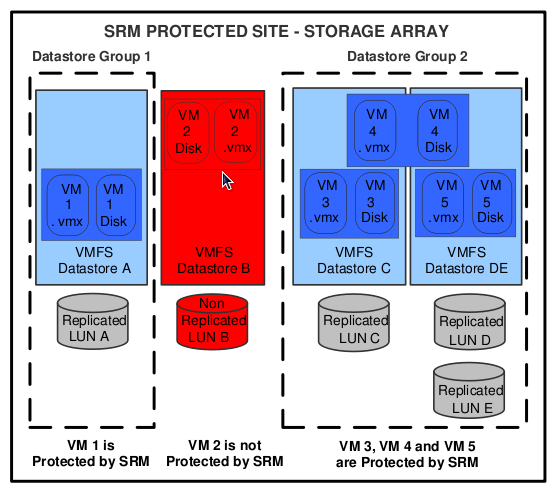
4. Protection Groups and Recovery Plans
- Creating Protection Groups: Logical groupings of VMs on replicated datastores.
- Defining Recovery Plans: Step-by-step instructions that SRM uses during failover, including boot order, dependencies, scripts, and IP customization rules.
These plans ensure that, during an actual disaster, systems are brought online in a controlled and predictable manner.
5. Testing and Validation
No DR setup is complete without rigorous testing. I used SRM's non-disruptive test recovery feature to validate:
- The integrity of the replication and recovery workflows.
- That VMs could successfully power on in the DR environment.
- Network connectivity and application availability post-failover.
This also included reverse replication and failback testing, confirming that operations could return to the production site smoothly after recovery.
Outcome
The SRM implementation was successful, and the DR site is now fully operational and ready to take over with minimal RTO/RPO in the event of an outage. The combination of VMware SRM and NetApp ISCSI storage provided a robust, scalable, and reliable disaster recovery solution tailored to our infrastructure.